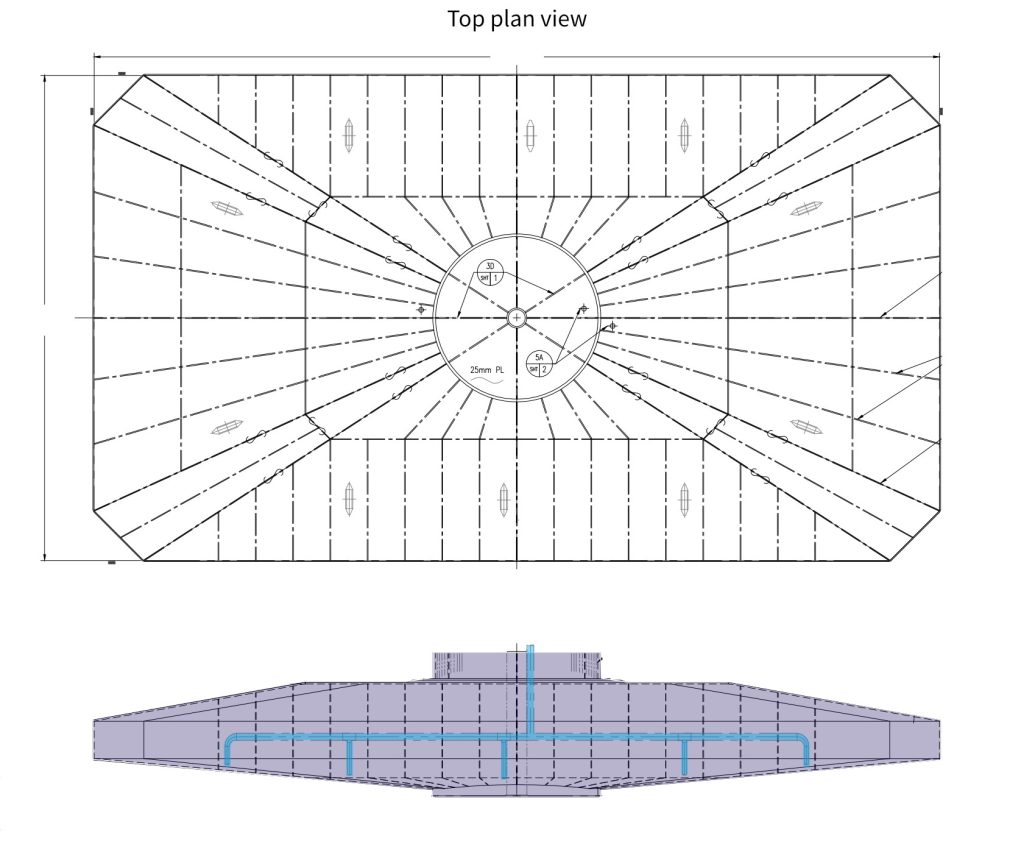
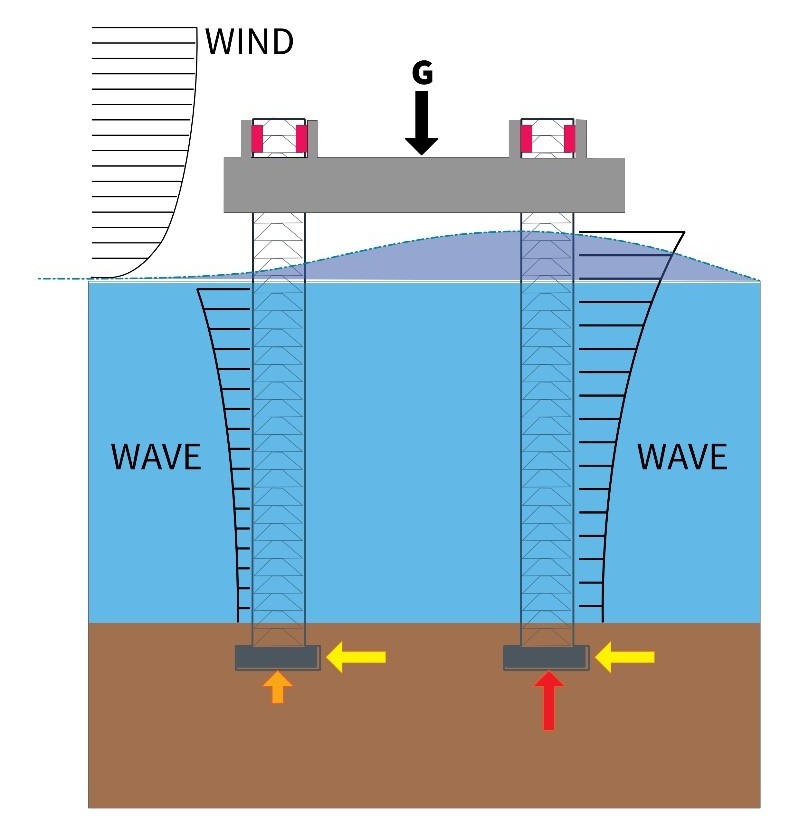
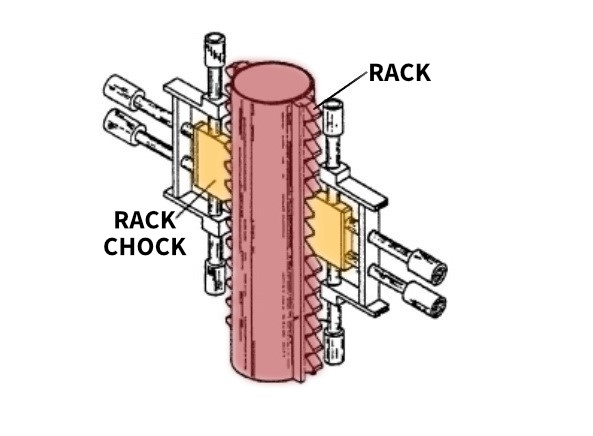
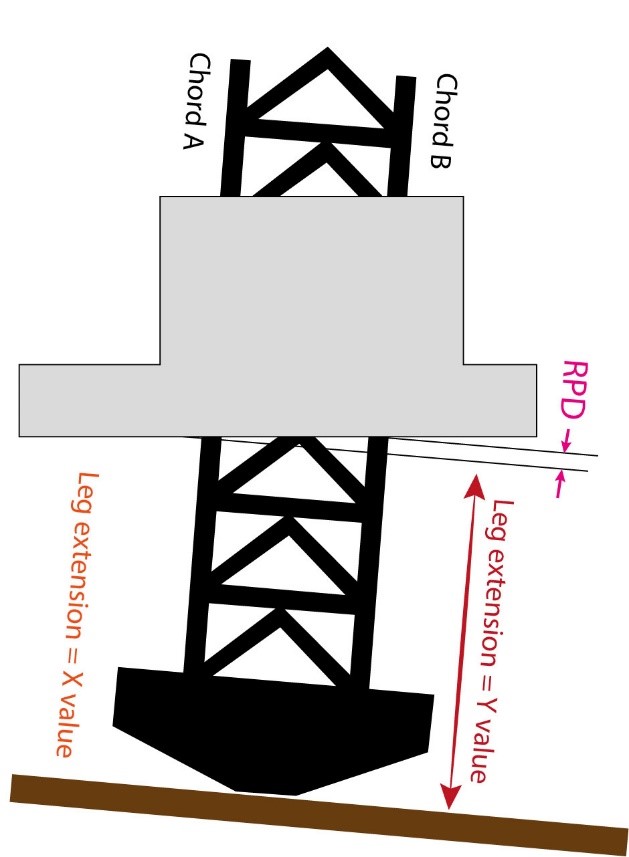
Jetting system
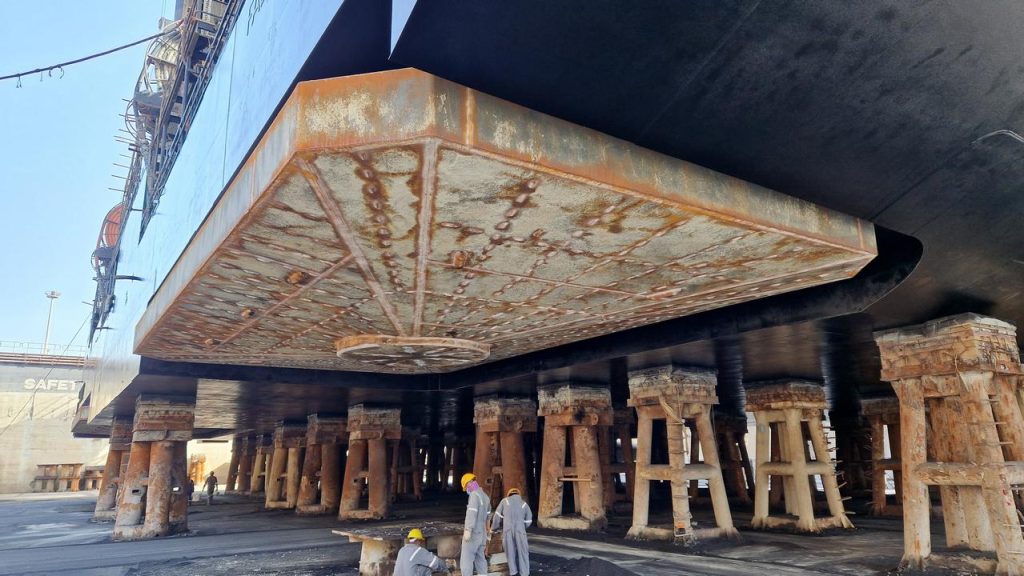
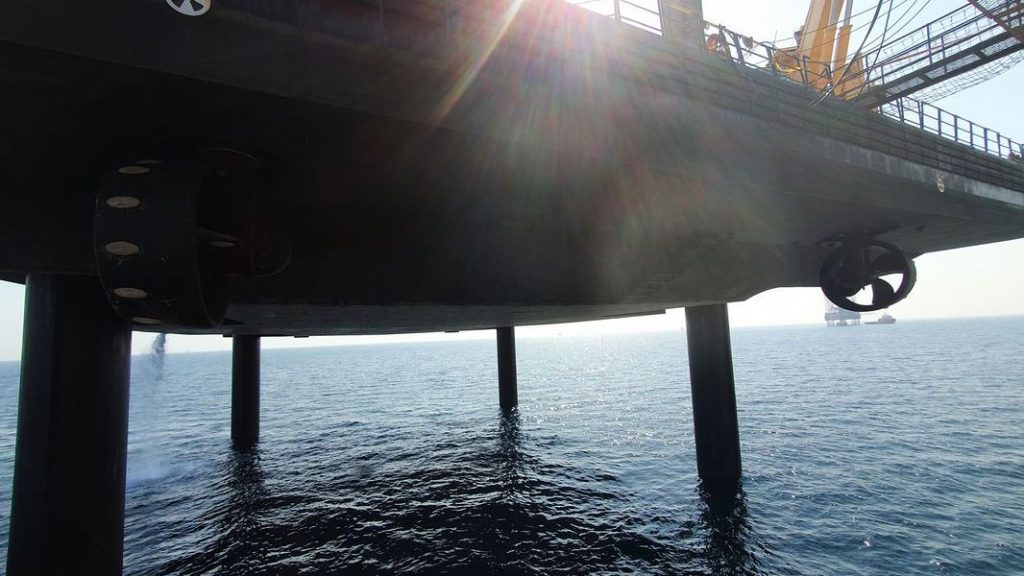
The penetration of the legs depends on the seabed type and its characteristics. Jetting systems are used to liberate the legs from the mud, when departing from the location. If Jackup is elevated on a location with a soft seabed, the penetration through the soil will be deep. It might be challenging to release the […]